Osteoporosis
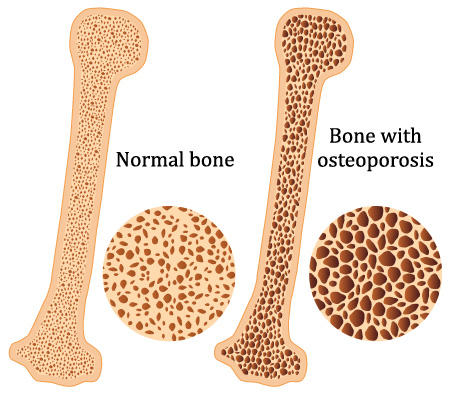
Osteoporosis is a disease in which decreased bone strength increases the risk of having broken bones. Women become at more risk of developing osteoporosis as a result of aging and especially after menopause.
Bones that commonly break include the bones of the back, forearm and hip. Bones become weak and can break with and without traumatic events. When osteoporosis is diagnosed, treatment is recommended because the consequences of these fractures can significantly affect quality of life.
How is osteoporosis diagnosed?
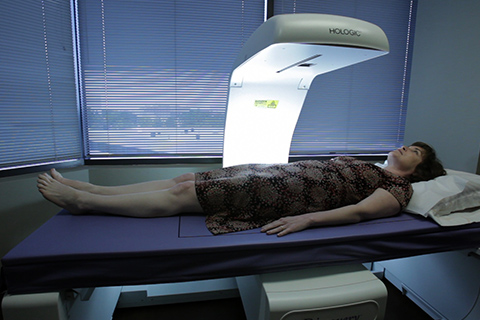
The most widely recommended method of diagnosing osteoporosis is the dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry study, more commonly known as a DXA scan of the lumbar spine and hip. This test measures bone mineral density. When a DXA scan is done, a T-score is assigned. A T-score of less than -2.5 at any of the measured sites establishes the diagnosis. The diagnosis can also be made in the setting of a low-trauma fracture even if a DXA scan has not been done.
What are treatment options for osteoporosis?
There are many treatment options for osteoporosis. When making a decision about the best treatment option, the risk and benefits of therapy must be weighed. Medications are also selected based on route of delivery, cost, or insurance coverage.
- Oral Bisphosphonates (Fosamax, Actonel, Boniva). Bisphosphonates are usually suggested as first-line therapy. These are oral medications that prevent the breakdown of bone and result in increased bone mineral density and decreased bone turnover. Each of these medications differs in dose frequency but can be taken weekly or monthly. Most need to be taken on an empty stomach with a full glass of water and patients need to remain in sitting or standing position for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication in order to avoid irritation of the esophagus. Side effects of bisphosphonates may include muscle aches and pains, nausea, heartburn and digestive ulcers.
- Intravenous Bisphosphonates (Reclast, Boniva). Reclast is an IV infusion that is administered every 1 to 2 years. Patients with renal dysfunction are not candidates for this medication. When given intravenously, Boniva is administered every 3 months.
- Drugs That Bind to Estrogen Receptors (Raloxifene). This is an oral, daily medication that has been shown to decrease spine fractures and is most useful for those who are at lower risk for hip fractures. It has also been shown to be beneficial in the reduction of risk for invasive breast cancer in postmenopausal women and those who are at high risk of breast cancer. Raloxifene can increase symptoms of hot flashes, the risk of developing blood clots in the lung or legs, and the risk of stroke.
- RANK Ligand Inhibitor (Prolia). This medication is given to postmenopausal women with osteoporosis who are at high risk of fracture due to severe osteoporosis. It is administered via injection under the skin every 6 months.
- Parathyroid Hormone (Forteo). This is a daily subcutaneous injection that can only be used for 24 months. It is usually reserved for patients who have severe osteoporosis (T score of less than -3.5 or T- score of -2.5 or below plus history of fracture). Its side effects include nausea, dizziness, muscle cramps, and hypercalcemia.
- Calcitonin (Fortical, Miacalcin). This medication is administered in the form of a nasal spray or injection under the skin and should not be used until women have been menopausal for 5 years. Potential side effects include flushing and nausea with the injection and nasal irritation with the nasal spray.
Are there any lifestyle changes that can help?

Exercise and adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D are good complements to medical therapy. Women with osteoporosis should set a goal of 30 minutes of weight-bearing exercise three times per week. Women who are getting adequate calcium from their diet do not need to take calcium supplements. However, women with inadequate dietary intake should take calcium supplements so that their total daily calcium take is about 1200 milligrams. Women should also ingest a total of 800 international units of vitamin D daily. In addition, patients with osteoporosis should also avoid smoking and heavy alcohol use and secure their homes so that falls can be prevented.
What tests can be done to determine if treatment is helping?
The DXA can be repeated in 1 or 2 years after initiation of treatment in order to determine the effect of treatment.
Our Locations
- NORTHSIDE OFFICE
 404-252-1137
404-252-1137
- EAST COBB OFFICE
 404-252-1137
404-252-1137
- JOHNS CREEK OFFICE
 404-252-1137
404-252-1137
- NORTHSIDE FORSYTH OFFICE
 404-252-1137
404-252-1137
Let's stay in touch
Our monthly newsletter keeps you up-to-date on healthy lifestyle, latest news, and our practice.